About LEMS
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a disorder of the neuromuscular junction8
Neuromuscular junction (NMJ) disorders may be the result of exposure to certain toxins, immune-mediated diseases, or genetic disorders.8
While all neuromuscular junction disorders are uncommon, the immune-mediated disorders—
LEMS and MG—are the ones most often encountered in the EMG lab.8

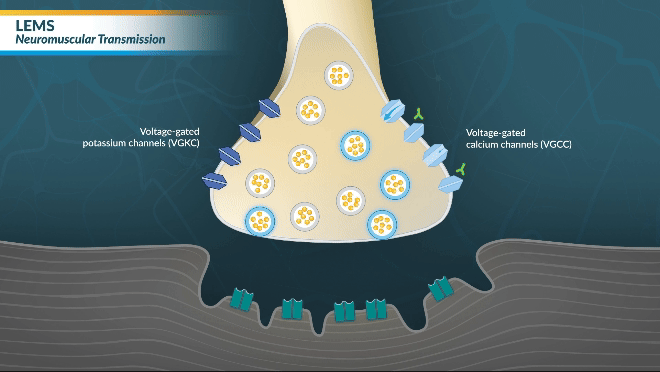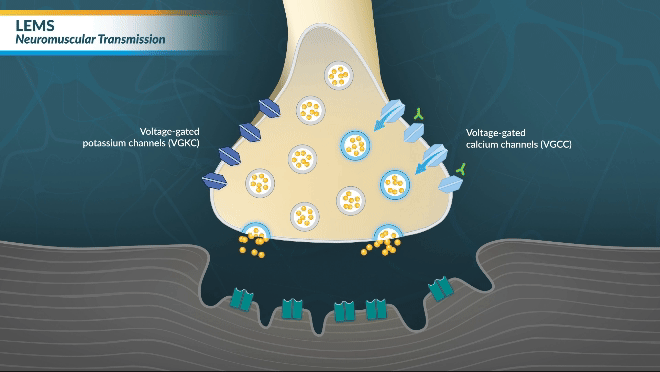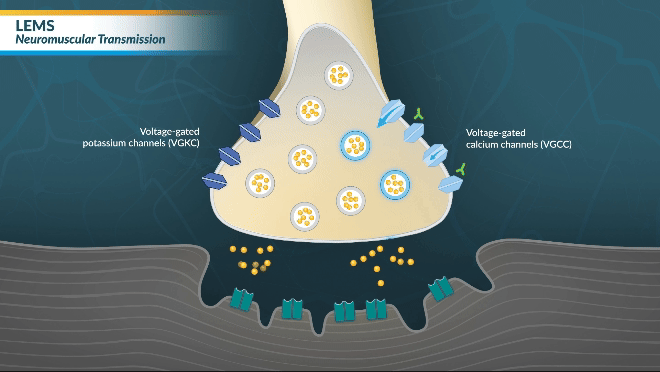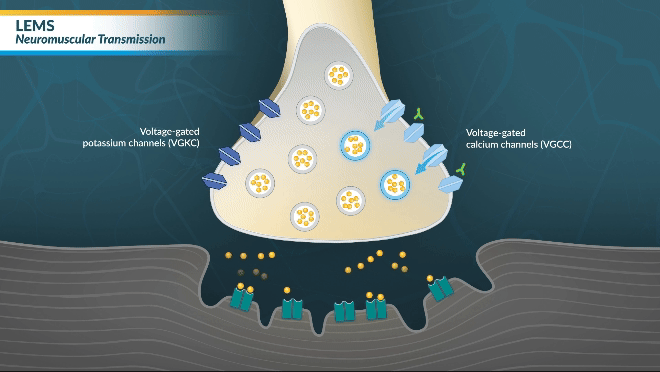
NORMAL NEUROMUSCULAR
FUNCTION
Watch this brief video animation to better understand the normal mechanism of action between neurons and muscle receptors.
KEY FACTS ABOUT LEMS
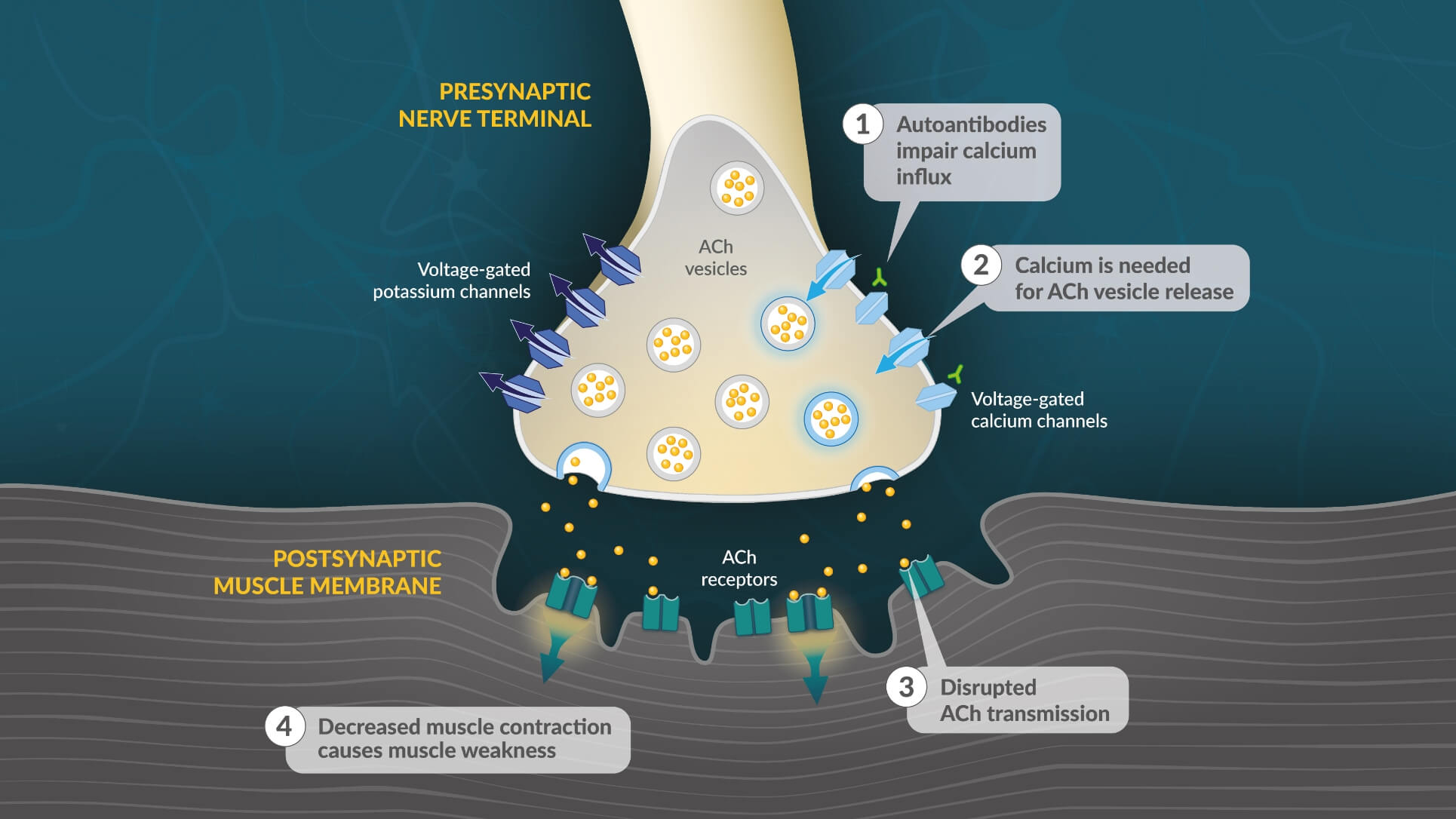
- In patients with LEMS, autoantibodies target voltage-gated calcium channels on the presynaptic motor neuron, reducing calcium influx during an action potential17
- Reduced intracellular calcium limits presynaptic vesicle fusion and release of ACh17
- Disrupted ACh transmission lessens activation of ACh receptors on the muscle fiber potential17
- Reduced ACh signaling results in diminished muscle fiber contraction and muscle weakness17
LEMS MECHANISM OF DISEASE
Watch this brief video animation to better understand how LEMS disrupts communication between neurons and muscle receptors
LEMS POP Quiz
LEMS is caused by: (select all that apply)
LEMS is caused by autoantibodies to presynaptic VGCCs that effectively decrease acetylcholine release and disrupt neuromuscular transmission, resulting in muscle weakness.17
DISEASE BURDEN
LEMS patients’ health-related quality of life is lower compared to MG patients and the general population18
A questionnaire-based survey compared the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS, n=46) with the HRQoL of patients living with myasthenia gravis (MG, n=92) and the general population (n=92).18
The results revealed that LEMS patients reported comparatively more unfavorable outcomes in the following domains18
Furthermore, patients with LEMS reported experiencing a higher overall burden of disease compared to patients with MG.18
Participants were also surveyed for satisfaction with LEMS treatments

BURDEN OF DISEASE FLASH CARD
Get a downloadable version of this content
and more using the link below.
Progression of LEMS symptoms contributes to worsening disease burden5
IN A 2012 SURVEY OF PATIENTS LIVING WITH LEMS5:
In a 2001 study, ~25% of LEMS patients required a wheelchair all the time or for mobilization outside the home19
A CHALLENGING DIAGNOSIS
LEMS patients often experience a long diagnostic journey5


REASONS FOR THE DELAYS IN DIAGNOSIS:
- Nonspecific and fluctuating symptoms12
- Slow progression of disease12
- Similar clinical presentation to other conditions12,20
Despite the significant burden it places on patients and their families, LEMS is often underrecognized5
THE DIAGNOSTIC CONUNDRUM
Studies reveal that more than half of patients with LEMS received a different diagnosis first12,20
In a cohort of 241 adult patients with LEMS, 58% were diagnosed with another disorder at least once before receiving the correct diagnosis.12
Clinical presentation of LEMS resembles other common diagnoses12,20
The symptoms of LEMS are often mistaken for common diseases and disorders, such as myasthenia gravis (MG), multiple sclerosis (MS), Guillain-Barré syndrome, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and depression.12,20
INITIAL DIAGNOSES PRIOR TO CONFIRMATION OF LEMS (n=140)12
- MG
- Muscular abnormalities
- Peripheral nerve abnormalities
- Intracranial/spinal cord abnormalities
- Depression
- Other
More than 1/3 of LEMS patients were previously diagnosed as having MG12
Prevalence of misdiagnoses among patients with LEMS12
- MG
- Muscular abnormalities
- Peripheral nerve abnormalities
- Intracranial/spinal cord abnormalities
- Depression
- Other
More than 1/3 of LEMS patients were previously diagnosed as having MG12
LEMS POP QUIZ
LEMS is often misdiagnosed as: (please select one)
The patient journey to a diagnosis of LEMS is often long and arduous.5 Reasons for the delay include the fact that the way LEMS presents is similar to all of the above conditions.12,20